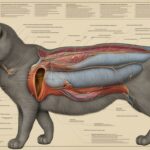
Cats’ sexual behavior and reproductive instincts are fascinating topics that many pet owners are curious about. In this article, we will explore the question “do cats get horny” and delve into the key aspects of feline sexual behavior, mating, and reproduction. We will discuss the factors that contribute to a cat’s sexual drive and explore their mating rituals and reproductive cycles.
Key Takeaways:
- Cats’ sexual behavior is influenced by hormones, instincts, and environmental factors.
- Their mating rituals include sexual signals and elaborate behaviors.
- Female cats go through a reproductive cycle known as the estrous cycle.
- Hormones and pheromones play a significant role in sexual attraction and communication.
- Neutering or spaying cats can reduce their sexual drive and prevent unwanted pregnancies.
Understanding Feline Sexual Behavior
Feline sexual behavior is a fascinating subject that involves a complex interplay of hormones, instincts, and environmental factors. Cats use various sexual signals to attract mates and engage in elaborate mating rituals. By understanding these behaviors, we can gain insight into a cat’s sexual instincts and preferences.
Sexual attraction in felines is often signaled through vocalizations, body postures, and scent marking. Female cats may exhibit behaviors such as yowling and rubbing against objects or individuals to communicate their receptivity. Male cats, on the other hand, may engage in mounting, spraying, and vocalizing to express their sexual interest. These signals not only help cats find potential mates but also establish and maintain social hierarchies within their territory.
During mating rituals, cats engage in playful and aggressive behaviors that serve to enhance sexual attraction and ensure successful copulation. They may engage in chasing, pouncing, and biting as part of their courtship behavior. These rituals allow cats to assess each other’s fitness for mating and establish a bond between potential partners.

Overall, understanding feline sexual behavior is not only intriguing but also crucial for cat owners. By recognizing the various sexual signals and rituals displayed by cats, we can better accommodate their natural instincts and ensure their overall well-being and happiness.
Understanding Sexual Signals
Sexual signals in cats are essential for communication and mate selection. Here are some common sexual signals that cats use:
- Vocalizations: Cats may yowl, meow, or purr to attract mates or express their interest.
- Body postures: Through their body language, cats communicate their receptivity or dominance. For example, a female cat may raise her tail and present her hindquarters, while a male cat may arch his back and puff up his fur to appear larger and more impressive.
- Scent marking: Cats have scent glands in various parts of their bodies, such as the face, paws, and anal area. They use these scent glands to deposit pheromones on objects or individuals, indicating their presence and availability for mating.
By recognizing and interpreting these signals, cat owners can better understand and respond to their feline companions’ sexual behavior.
The Reproductive Cycle of Cats
Understanding the reproductive cycle of cats is essential for cat owners to provide proper care and support. Female cats go through a series of stages known as the estrous cycle, which prepares them for mating and reproduction. This cycle consists of proestrus, estrus, metestrus, diestrus, and anestrus, each characterized by specific hormonal changes and behaviors.

During proestrus, which typically lasts for one to two days, female cats experience preliminary changes such as increased friendliness and restlessness. This stage prepares the body for mating. It is followed by estrus, often referred to as the “heat” phase, which can last anywhere from four to seven days. During estrus, female cats become sexually receptive and may exhibit behaviors such as frequent vocalization and rubbing against objects or people.
After estrus, the cat enters the metestrus stage, which is a short period of sexual inactivity. The diestrus stage follows, during which the cat may experience a false pregnancy if she did not mate. Finally, the anestrus stage marks the period of sexual inactivity, often lasting for several weeks or months.
Hormonal Fluctuations and Behavioral Changes
Throughout the reproductive cycle, hormonal fluctuations play a vital role in a cat’s behavior and physiology. The levels of estrogen and progesterone rise and fall, triggering specific behaviors and physical changes. These hormonal fluctuations can influence a cat’s mood, appetite, and overall behavior. It is crucial to monitor these changes and provide appropriate care and support during each stage of the reproductive cycle.
| Stage | Hormonal Changes | Behavioral Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Proestrus | Rise in estrogen | Restlessness, increased friendliness |
| Estrus | Peak in estrogen | Sexual receptivity, vocalization, rubbing |
| Metestrus | Decline in estrogen | Sexual inactivity |
| Diestrus | Progesterone dominates | False pregnancy (if not mated) |
| Anestrus | Low hormone levels | Sexual inactivity |
By understanding the different stages of the reproductive cycle and their associated hormonal and behavioral changes, cat owners can better support their pets’ health and well-being. Monitoring the cat’s behavior, providing a safe and comfortable environment, and seeking veterinary care when needed can contribute to a successful and healthy reproductive cycle.
The Role of Hormones and Pheromones
In understanding feline sexual behavior, it is essential to recognize the significant role that hormones and pheromones play. Hormones, such as testosterone in males and estrogen in females, are responsible for regulating a cat’s sexual arousal and receptivity. These hormones influence their behavior and drive to mate.
Additionally, pheromones play a crucial role in sexual attraction and communication between cats. These chemical signals are secreted by cats and can be detected by other cats in their environment. Pheromones provide information about a cat’s reproductive status and can potentially trigger sexual behaviors.
Hormones and pheromones work together to create a complex network of sexual cues and signals in cats. These chemical messengers help cats communicate their sexual availability and preferences. Understanding the role of hormones and pheromones is crucial for comprehending feline sexual behavior and addressing any related concerns.

Effects of Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, can have a noticeable impact on a cat’s behavior. Cats may experience increased energy levels and sporadic arousals due to the rise and fall of hormone levels. It is essential for cat owners to appreciate these changes and adjust their interactions and environment accordingly.
“Understanding the role of hormones and pheromones is crucial for comprehending feline sexual behavior and addressing any related concerns.”
By recognizing and managing hormonal fluctuations, cat owners can provide a supportive and stable environment for their pets. Engaging in play, providing mental and physical stimulation, and ensuring a consistent routine can help alleviate any behavioral challenges associated with hormonal changes.
Conclusion
The interplay between hormones and pheromones shapes feline sexual behavior and drives mating instincts. Understanding these biological factors can help cat owners navigate their pet’s sexual needs and create a harmonious environment. By acknowledging the role of hormones and pheromones, we can cultivate a deeper understanding of cats‘ innate behaviors and promote their overall well-being.
Intact Cats vs. Neutered/Spayed Cats
One of the key decisions that cat owners face is whether to have their cats neutered or spayed. This decision can significantly impact a cat’s sexual behavior and reproductive instincts. Intact cats, which are not neutered or spayed, tend to exhibit more intense sexual behaviors and instincts compared to their neutered or spayed counterparts.
Neutering or spaying a cat involves the removal of their reproductive organs, such as the testes in male cats or the uterus and ovaries in female cats. This procedure can significantly reduce a cat’s sexual drive and eliminate the risk of unwanted pregnancies. Additionally, neutering or spaying can prevent certain health issues, such as uterine, ovarian, and mammary gland cancers in female cats, and testicular cancer in male cats.
Benefits of Neutering or Spaying
There are several benefits to neutering or spaying cats:
- Reduces the risk of certain cancers: Neutering or spaying can significantly reduce the risk of reproductive-related cancers in cats, improving their overall health and longevity.
- Eliminates unwanted behaviors: Intact cats may exhibit undesirable behaviors associated with their sexual instincts, such as aggressive behavior, roaming, marking territory with urine, and yowling. Neutering or spaying can help mitigate or eliminate these behaviors.
- Controls feline populations: By neutering or spaying cats, pet owners can contribute to controlling the feline population and reducing the number of stray or homeless cats.

| Behavior | Intact Cats | Neutered/Spayed Cats |
|---|---|---|
| Marking territory with urine | More likely to engage in this behavior | Less likely to engage in this behavior |
| Roaming | Tendency to roam in search of mates | Less likely to roam |
| Aggressive behavior | More likely to exhibit aggressive behavior towards other cats | Less likely to exhibit aggressive behavior |
| Yowling | More vocal during mating season | Less likely to vocalize excessively |
Table: A comparison of behaviors between intact cats and neutered/spayed cats
It is important for cat owners to consider the benefits of neutering or spaying their cats. By doing so, they can help promote their cats’ overall well-being, prevent unwanted litters, and contribute to controlling the feline population. Consultation with a veterinarian is recommended to determine the appropriate timing for neutering or spaying based on the individual cat’s age and health.
Factors That Influence Sexual Behavior
When it comes to feline sexual behavior, several factors come into play that can influence a cat’s mating preferences, sexual competition, and reproductive success. Understanding these factors can provide valuable insights into why cats behave the way they do.
Sexual Maturity
One of the primary factors that influence a cat’s sexual behavior is sexual maturity. Cats typically reach sexual maturity between six and nine months of age, although this can vary depending on the breed and individual cat. Once a cat reaches sexual maturity, their hormones kick in, and they become more receptive to mating.
Sexual Preferences
Just like humans, cats can develop sexual preferences. Some cats may be attracted to certain traits or behaviors in potential mates, while others may have a more diverse range of preferences. These preferences can influence a cat’s mate choice and the likelihood of successful mating.
Sexual Competition
Cats are known for their territorial nature, and this extends to their sexual behavior as well. Sexual competition between male cats can be intense, with dominant males often fighting for access to females. This competition can influence a cat’s sexual behavior and the strategies they use to increase their chances of mating.
Reproductive Success
Reproductive success is the ultimate goal of feline sexual behavior. Cats have evolved various strategies to increase their chances of reproductive success, from attracting mates through vocalizations and scent marking to engaging in elaborate mating rituals. These behaviors help ensure the survival of their genes and the continuation of their species.
Understanding the factors that influence a cat’s sexual behavior can help us better comprehend their instincts and behaviors. It is important to provide a safe and conducive environment for cats to express their natural sexual behaviors while also considering responsible reproductive practices to maintain their well-being.

Common Sexual Behaviors in Cats
When it comes to sexual behaviors, cats can exhibit a range of interesting and sometimes perplexing actions. Understanding these behaviors is crucial for cat owners to provide appropriate care and ensure a harmonious living environment. Let’s explore some of the most common sexual behaviors observed in cats.
Mounting
One of the most well-known sexual behaviors in cats is mounting, where a male cat positions itself on top of another cat, whether male or female. This behavior is not limited to sexual interactions and can also be a display of dominance or a way to establish territory.
Spraying
Cats have scent glands located in their anal region that they use for marking their territory. Spraying is a behavior that involves the cat releasing a small amount of urine, often against vertical surfaces, to mark its territory. Male cats are more likely to spray, but females can also exhibit this behavior.
Yowling
Yowling is a vocalization commonly heard during the mating season. Both male and female cats may engage in yowling to attract potential mates. This vocalization can be quite loud and can sometimes be mistaken for distress or fighting.
Scratching
Scratching is a natural behavior for cats that serves multiple purposes, including maintaining their claws, stretching their muscles, and marking their territory. Cats may also engage in scratching as a way to display their sexual availability to potential mates.
Territorial Behavior and Scent Marking
Cats are territorial animals, and they use scent marking as a way to establish and maintain their territory. This behavior involves rubbing their scent glands against objects or surfaces to leave their unique scent. It serves as a form of communication to other cats, conveying messages about their sexual availability and marking boundaries.

| Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Mounting | A male cat positioning itself on top of another cat as a display of dominance or to establish territory. |
| Spraying | The release of a small amount of urine, often against vertical surfaces, to mark territory. |
| Yowling | Loud vocalization used to attract potential mates during the mating season. |
| Scratching | Natural behavior that helps cats maintain their claws, stretch their muscles, and mark territory. |
| Territorial Behavior and Scent Marking | Rubbing scent glands against objects or surfaces to leave their unique scent and communicate with other cats. |
Health Issues Related to Sexual Behavior
When it comes to feline sexual behavior, there are certain health issues that pet owners should be aware of. Frequent or abnormal sexual behaviors in cats can sometimes indicate underlying health problems that require attention. Three common health issues related to sexual behavior in cats are urinary tract infections, neurological problems, and debris in the genital region.
Urinary tract infections can occur when bacteria enter the urethra or bladder, causing discomfort and potentially leading to more serious complications. Cats with urinary tract infections may exhibit changes in their sexual behavior, such as frequent urination or straining while urinating. It is crucial to seek veterinary assistance if you notice any signs of urinary tract infections in your cat, as prompt treatment is essential to prevent further complications.
Neurological problems can also impact a cat’s sexual behavior. Conditions such as nerve damage or spinal cord injuries can affect the cat’s ability to engage in normal sexual behaviors, leading to changes or abnormalities. If you suspect that your cat is experiencing neurological issues, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
In some cases, debris can become trapped in the genital region, causing discomfort and affecting sexual behavior. This debris may be the result of poor hygiene or the presence of foreign objects. Regular grooming and keeping the genital area clean can help prevent debris buildup. If you notice any unusual discharge or debris in your cat’s genital region, it is important to have them examined by a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.

In summary, while sexual behavior in cats is a natural part of their instincts and reproductive cycle, it is essential to monitor for any abnormal or frequent behaviors that could indicate underlying health issues. Urinary tract infections, neurological problems, and debris in the genital region are potential health concerns that can impact a cat’s sexual behavior. Seeking veterinary assistance and proper treatment is crucial for maintaining your cat’s overall health and well-being.
The Impact of Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal changes during puberty can have a significant impact on a cat’s behavior. Just like humans, cats experience fluctuations in their hormonal levels as they reach sexual maturity. These changes can result in increased energy levels and sporadic arousals in cats. It is important for cat owners to understand and manage these hormonal fluctuations to ensure the overall well-being of their feline companions.
Puberty in cats typically occurs between the ages of 5 to 9 months. During this period, the production of reproductive hormones such as testosterone in male cats and estrogen in female cats increases. This surge in hormones can lead to changes in behavior, including increased playfulness, restlessness, and a heightened interest in exploring their surroundings.
For pet owners, it is essential to provide a stimulating environment and engage in interactive play sessions with their cats to channel their energy in a positive way. Regular exercise, such as interactive toys and playtime, can help satisfy their natural instincts and prevent behavioral issues that may arise from hormonal fluctuations.
The Role of Environmental Enrichment
In addition to physical exercise, environmental enrichment plays a crucial role in managing hormonal fluctuations in cats. Providing a stimulating and enriching environment can help alleviate any frustrations or restless behavior that may result from hormonal changes.
Enrichment can include providing scratching posts, interactive toys, safe climbing structures, and hiding spots for cats to explore and engage in natural behaviors. Creating a safe and enriching environment can help cats cope with the hormonal fluctuations during puberty and ensure a smoother transition into adulthood.
Conclusion
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty are a natural part of a cat’s development. Understanding and managing these changes is crucial for cat owners to ensure their feline companions’ well-being. By providing a stimulating environment, engaging in regular play sessions, and offering appropriate outlets for their natural behaviors, cat owners can help their cats navigate this hormonal transition period with ease.
Tips for Managing Petting Sessions
Petting sessions with cats can be a delightful way to bond and show affection. However, it’s important to understand that each cat has its own preferences and boundaries when it comes to physical contact. By observing their body language and respecting their individual needs, you can create a positive and enjoyable experience for both you and your furry friend.
1. Read Their Body Language
Cats communicate through their body language, and it’s essential to pay attention to their cues during a petting session. Look for signs of relaxation, such as soft purring, slow blinking, and a relaxed posture. On the other hand, if your cat starts to twitch its tail, flatten its ears, or show signs of aggression, it’s a sign that they may be feeling overwhelmed or uncomfortable. In such cases, it’s best to give them space and allow them to approach you when they’re ready.
2. Set Clear Boundaries
While some cats enjoy being stroked all over their body, others may have specific areas they prefer to be petted or limits to their tolerance. Pay attention to your cat’s reactions and find out their favorite spots by gently stroking different areas and observing their response. Respect their boundaries and avoid petting them in areas where they show signs of discomfort. This will help maintain a positive association with petting sessions and prevent any unintended negative experiences.
3. Incorporate Play into Petting Sessions
Engaging in interactive play before and during a petting session can help redirect your cat’s energy and make them more receptive to touch. Use toys, such as feather wands or laser pointers, to stimulate their natural hunting instincts and allow them to release any pent-up energy. This can create a more relaxed and conducive environment for petting and bonding.
4. Use Gentle Strokes and Positive Reinforcement
When petting your cat, use gentle and slow strokes to create a soothing and calming effect. Avoid applying too much pressure or pulling on their fur, as this can cause discomfort. Additionally, incorporate positive reinforcement by offering treats or rewards during and after petting sessions. This will reinforce positive behavior and further strengthen the bond between you and your cat.
5. Provide a Comfortable Environment
Creating a peaceful and comfortable environment can enhance the quality of petting sessions. Choose a quiet location where your cat feels safe and secure. Ensure that the room is free from any potential distractions or sources of stress, such as loud noises or other pets. By providing a serene environment, you can help your cat relax and fully enjoy the affectionate experience.

Remember, every cat is different, so it’s essential to be patient and adaptable when it comes to petting sessions. By respecting their boundaries, reading their body language, and creating a positive and stimulating environment, you can foster a strong and loving relationship with your feline companion.
The Importance of Spaying Female Cats
Spaying female cats is a crucial aspect of their reproductive health. It involves the surgical removal of the ovaries and uterus to prevent unwanted pregnancies. However, the benefits of spaying go beyond population control. Spaying significantly reduces the risk of serious health issues in female cats, including uterine, ovarian, and mammary gland cancer.
Female cats that are not spayed are at a higher risk of developing reproductive cancers. Spaying eliminates the risk of uterine infections, also known as pyometra, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. By spaying your cat, you can ensure her long-term health and wellbeing.
The procedure itself is safe and commonly performed by veterinarians. It is typically done when the cat is around six months old, but it can be done earlier or later depending on the veterinarian’s recommendation. Spaying not only provides health benefits for your cat but also helps reduce the number of homeless and abandoned cats in shelters.
It’s important to note that spaying does not alter a cat’s personality or behavior. While it may help reduce certain territorial and mating behaviors, it does not fundamentally change the cat’s nature. Spaying is a responsible decision that can improve your cat’s overall quality of life and ensure a healthier future.

The Benefits of Spaying:
- Reduces the risk of reproductive cancers
- Prevents uterine infections (pyometra)
- Avoids unwanted pregnancies
- Improves long-term health and wellbeing
- Helps control the cat population
“Spaying female cats is a responsible decision that can improve their overall quality of life and ensure a healthier future.”
By choosing to spay your female cat, you are taking an important step in protecting her reproductive health and overall well-being. Consult with your veterinarian to discuss the best timing for the procedure and address any questions or concerns you may have. Spaying is not only beneficial for your cat but also contributes to the welfare of cats as a whole.
Understanding Anal Gland Expression
When it comes to understanding our feline companions, one aspect that often raises questions and curiosity is anal gland expression. Cats have anal glands, also known as anal sacs, which produce an oily substance used for marking behavior. These tiny sacs, located near the cat’s anus, play a vital role in communication through the release of pheromones and scent marking.
Anal gland expression is a natural behavior in cats. It allows them to mark their territory, communicate with other cats, and establish their presence. By releasing pheromones through the anal glands, cats leave invisible scent messages that provide information about their age, sex, and overall identity.
As responsible pet owners, it is important to understand this behavior and provide appropriate care for our feline friends. Regular anal gland expression is necessary for some cats, while others may naturally take care of it through their normal routines. However, improper or incomplete expression can lead to health issues such as impacted anal sacs, infection, discomfort, incontinence, or even behavioral concerns.
By being aware of anal gland expression and monitoring our cat’s behavior, we can ensure their well-being and address any potential issues promptly. If you notice any changes in your cat’s anal gland behavior or suspect an issue, it is best to consult with a veterinarian who can provide guidance and recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.

Understanding anal gland expression is just one aspect of feline behavior that contributes to our overall understanding of our furry friends. By delving into these behaviors, we can strengthen the bond with our cats and provide them with the care they need to thrive.
Possible Issues with Anal Gland Expression
Problems can arise when the anal glands of cats are not properly expressed. One common issue is the development of impacted anal sacs, which occurs when the glands become clogged and unable to release their contents. This can lead to discomfort and even pain for the cat.
In addition to impaction, infections can also occur in the anal glands. Bacteria can enter the glands through small tears or openings, causing inflammation and infection. This can further exacerbate the discomfort and lead to more serious health problems if left untreated.
Impacted anal sacs and infections can result in symptoms such as scooting or dragging the bottom along the floor, excessive licking or biting of the anal area, and foul-smelling discharge. In some cases, the cat may experience incontinence or changes in behavior due to the discomfort and pain associated with these issues.

Normalizing the Discussion of Feline Anal Gland Expression
When it comes to cat behavior and health, there are certain topics that may carry a certain stigma or discomfort. One such topic is feline anal gland expression. However, by normalizing the discussion around this important aspect of cat health, we can help increase awareness and understanding among cat owners.
Communication is key when it comes to understanding our feline companions. By openly discussing topics like anal gland expression, we can demystify certain behaviors and prevent misunderstandings. This can lead to better care for cats and a deeper appreciation for their unique needs and instincts.
Increasing awareness about feline anal gland expression is crucial for cat owners. By understanding the purpose and importance of anal glands, we can take appropriate measures to ensure our cats’ health and well-being. This includes recognizing the signs of impacted or infected anal glands and seeking veterinary assistance if necessary.
Let’s work together to break the stigma surrounding feline anal gland expression and promote open discussions about cat health and behavior. By doing so, we can create a more informed and compassionate community of cat owners who prioritize the well-being of their feline friends.

The Importance of Open Dialogue
Opening up about feline anal gland expression allows us to address concerns and provide the best care for our cats. By discussing this topic openly, we can learn from one another’s experiences and share valuable insights. Together, we can remove the stigma associated with anal gland expression and create a supportive environment for cat owners.
Creating a Safe and Comfortable Space
Creating a safe and comfortable space for discussing feline anal gland expression is essential. This means approaching the topic with empathy, understanding, and a willingness to learn. By fostering an environment where questions can be asked without judgment, we can encourage cat owners to seek advice and share their experiences.
Empowering Cat Owners
Open discussions about feline anal gland expression empower cat owners to take an active role in their cats’ health. By providing information and resources, we can help cat owners understand the signs and symptoms of anal gland issues, as well as the appropriate steps for prevention and treatment. Together, we can ensure that cats receive the care they need and deserve.
Conclusion
Understanding feline sexual behavior and the reproductive cycle is essential for cat owners like me. By delving into the key aspects of feline sexual behavior, mating, and reproduction, we can better comprehend our furry companions’ needs and ensure their overall well-being.
From studying feline sexual behavior, I’ve learned that cats’ instincts and preferences are influenced by a complex interplay of hormones, instincts, and environmental factors. Their elaborate mating rituals and sexual signals provide insights into their sexual attraction and preferences. Additionally, recognizing the stages of the reproductive cycle, such as estrus, proestrus, metestrus, diestrus, and anestrus, helps us understand the physical and behavioral changes that occur.
Understanding the role of hormones and pheromones in feline sexual behavior is crucial. Hormones like testosterone and estrogen regulate a cat’s sexual drive and receptivity. Pheromones, on the other hand, play a significant role in sexual attraction and communication between cats.
While intact cats exhibit more intense sexual behaviors, neutering or spaying can reduce their sexual drive and prevent unwanted pregnancies. It is important to consider the benefits of neutering or spaying to control feline populations and prevent certain health issues.
To ensure our cats’ well-being, it’s important to be aware of the factors that influence their sexual behavior, monitor their health for any underlying issues, and provide appropriate care. By normalizing discussions about feline sexual behavior and reproductive health, we can increase awareness, dispel stigmas, and foster a better understanding of our feline companions.
In conclusion, by understanding and addressing feline sexual behavior, mating, and the reproductive cycle, we can nurture a healthy bond with our cats and ensure their long-term happiness and well-being.
FAQ
Do cats get horny?
Yes, cats can experience sexual arousal and display behaviors associated with mating when they are in heat.
What factors influence a cat’s sexual behavior?
Sexual maturity, mate choice, sexual competition, and reproductive success all play a role in a cat’s sexual behavior.
What are some common sexual behaviors in cats?
Cats may engage in mounting, spraying, yowling, scratching, and territorial behavior as part of their sexual behavior.
Can frequent or abnormal sexual behaviors in cats indicate health issues?
Yes, changes in sexual behaviors can sometimes be a sign of underlying health issues such as urinary tract infections or neurological problems.
Should female cats be spayed?
Yes, spaying female cats is important for their reproductive health and helps reduce the risk of certain cancers.
What are anal glands and why are they important for cats?
Anal glands are small sacs located near a cat’s anus that produce an oily substance used for marking behavior and communication with other cats.
What can happen if a cat’s anal glands are not properly expressed?
If a cat’s anal glands are not properly expressed, they can become impacted or infected, leading to discomfort, incontinence, or behavior concerns.
How can we normalize the discussion of feline anal gland expression?
By openly discussing this topic, we can increase awareness and understanding among cat owners, leading to better care and overall feline health.